
Researchers from the Hefei Institute of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have identified a key molecular module that regulates rice plant architecture, providing valuable genetic resources and regulatory modules for molecular breeding.
Researchers from the Yunnan Observatories of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have conducted a new study on the temporal evolution of the afterglow from gamma-ray burst GRB 240825A. The study offers new evidence to better understand the physical environment surrounding gamma-ray bursts and provides insights into the mechanisms that govern their afterglow emission.

A research team from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, in collaboration with researchers from Anhui University, ShanghaiTech University, and the University of New Hampshire, has demonstrated the first electrically controllable generation of hopfions, three-dimensional topological solitons, in a solid-state magnetic system.
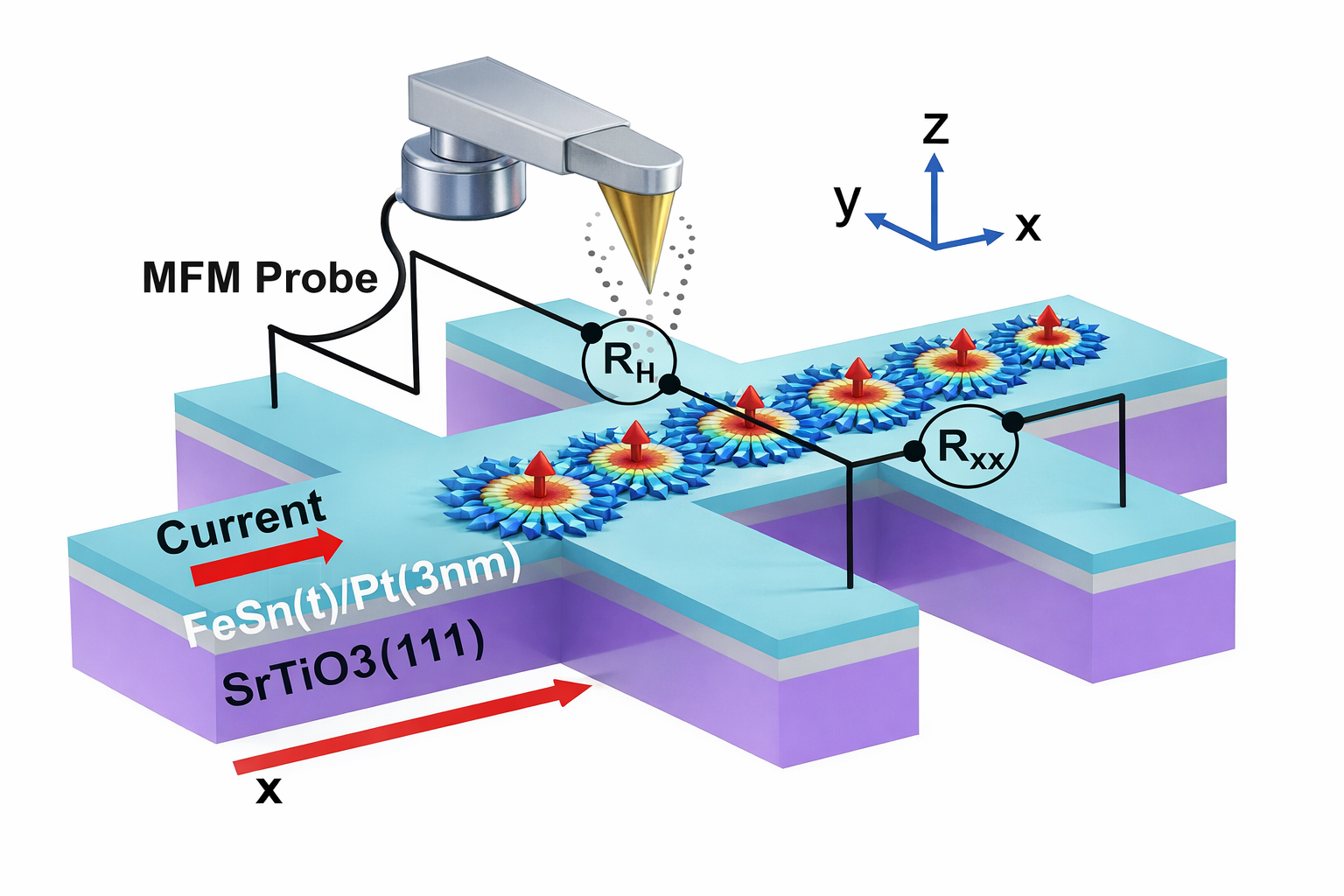
Researchers from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, in collaboration with researchers from the Institute of Semiconductors, revealed anomalous oscillatory magnetoresistance in an antiferromagnetic kagome semimetal heterostructure and directly identified its corresponding topological magnetic structures.
A research team from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science has grew a high-entropy garnet-structured oxide crystal and achieved enhanced laser performance at the 2.8 μm wavelength band. By introducing a high-entropy design into a garnet crystal system, the researchers obtained a wide emission band near 2.8 μm and continuous-wave laser output with improved average power and beam quality.

A research team led by Profs. WU Zhikun and ZHUANG Shengli from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with Professor LU Zhou from Anhui Normal University, has proposed an instant "anti-galvanic reduction" alloying strategy for the synthesis of large silver nanoclusters.

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

